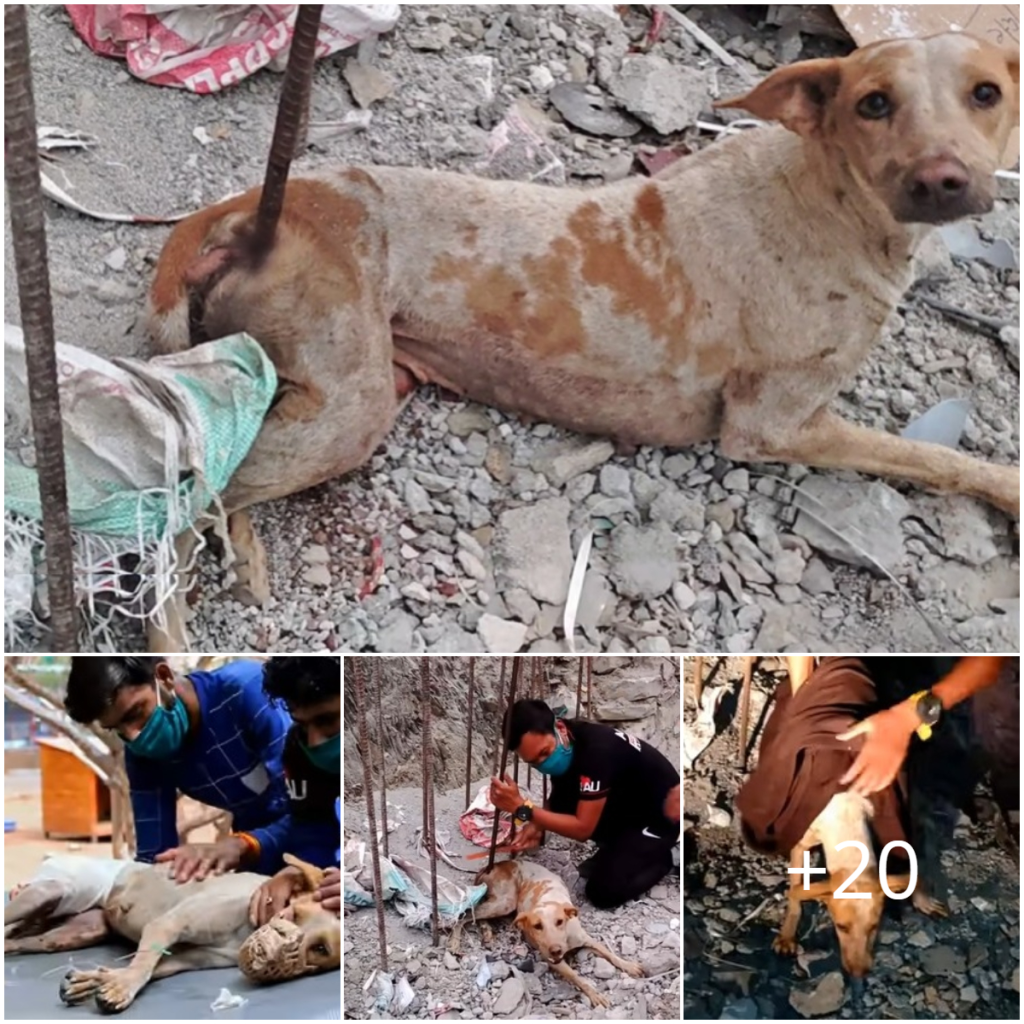

It is heartbreaking to hear that a dog was impaled by a stick. The animal had to go through tremendous agony and suffering before being saved. However, the road to recovery can be beautiful, and the dog can recover completely with proper care and attention.

When a dog gets impaled by a rod, the first goal is to get the item out of the dog’s way as soon and safely as possible. This may need surgery or other medical intervention, and it is critical to seek emergency veterinarian care to maintain the animal’s stability and safety.

After the dog’s immediate medical needs have been met, it is critical to concentrate on his long-term recovery. This may include giving patients pain relievers, wound care, and other medical treatments as required.
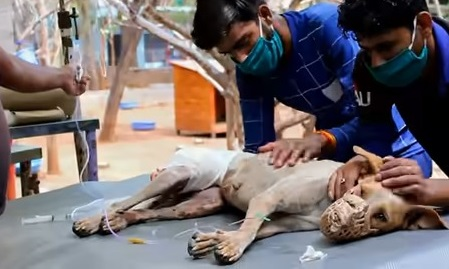
Additionally, to help the dog cope with the trauma of the experience, it is critical to provide emotional support and care. Following such a traumatic event, dogs may experience anxiety, fear, and other emotional distress, and it is critical to provide them with a calm and nurturing environment to help them feel safe and secure.

Professional assistance from a trained dog trainer or behaviorist may also be required to assist the dog in overcoming emotional trauma and rebuilding trust in people. Positive reinforcement training approaches might make the dog feel more secure and comfortable.

It’s essential to note that recovering from such a traumatic incident takes time and patience, but with the right care and attention, dogs like the one that was poked may make a full recovery. They may rediscover the ability to trust and love, and live happy and full lives with their new families.

”Is He Ok?” Tom Hanks Shocks Fans in New Look — Fans Are Worried
Tom Hanks and his wife, Rita Wilson, once again proved that they are one of Hollywood’s most iconic and solid couples as they attended a gala in Beverly Hills. Hanks radiated charm and Hollywood glamour, but it was a significant transformation in his look that drew a lot of attention.
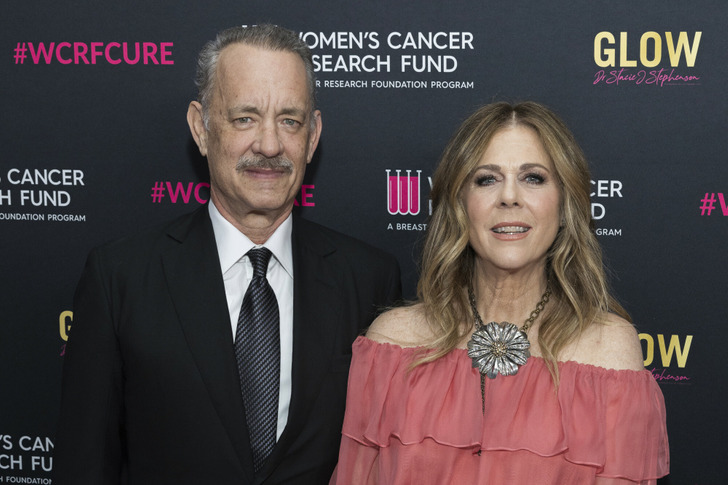

The Women’s Cancer Research Fund hosted its prominent annual fundraiser, “An Unforgettable Evening,” at the Beverly Wilshire in Beverly Hills.
Among the many celebrities who added their star power to the event were Tom Hanks, 67, and his wife, Rita Wilson, 67, who serve as honorary chairs.
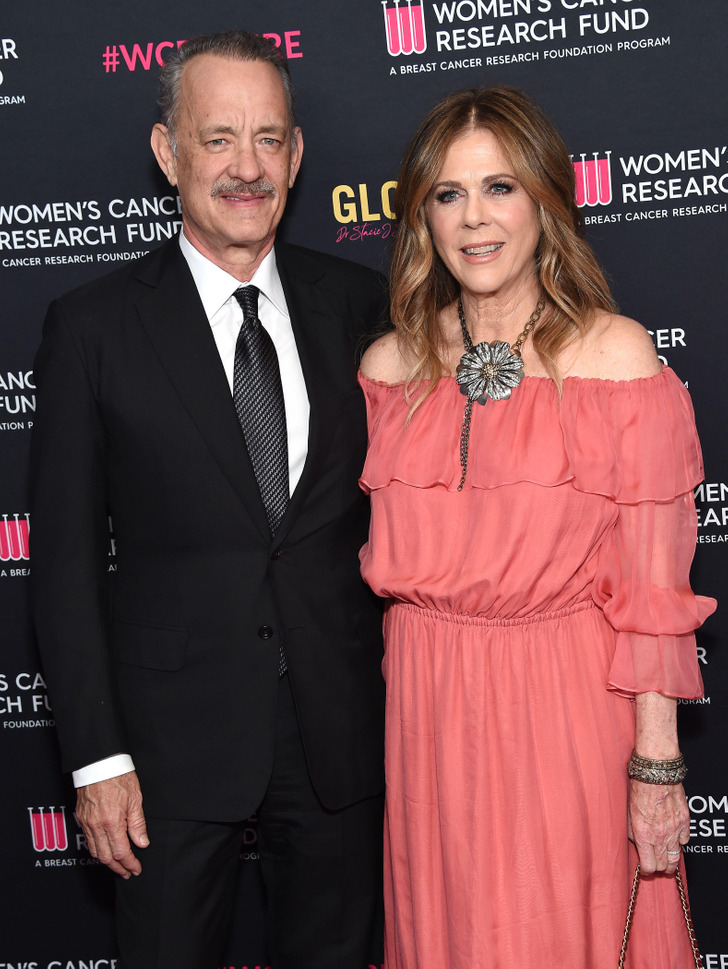

Upon their arrival, the Forrest Gump actor commanded attention before the cameras, accompanied by his wife. He donned an impeccable black ensemble, featuring a crisp white shirt, a striking, black-patterned tie, and coordinating shoes.
Wilson stood beside her husband in a vibrant pinkish-red dress, featuring an off-the-shoulder design and a cinched waist.
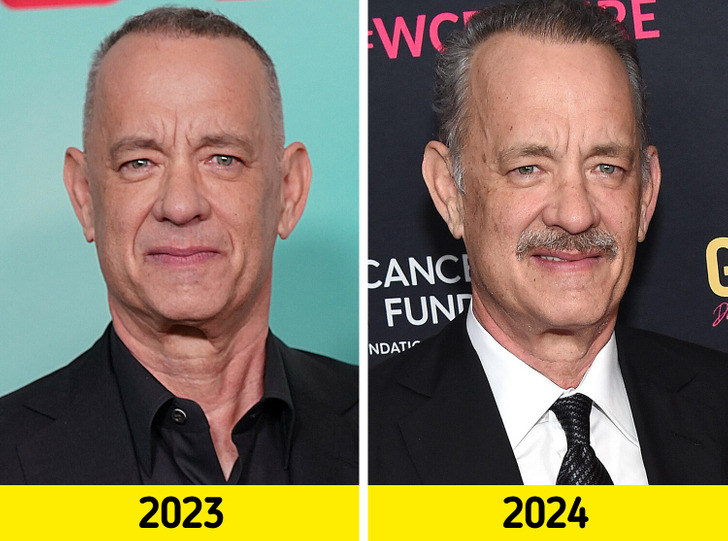
Hanks showcased a fresh, short haircut, highlighting his salt-and-pepper hair, but what truly caught everyone’s attention was his mustache—a rare and striking look for him.
But many fans were worried about the star and thought that he didn’t look in the best shape. One person wondered, “Is he OK???” Another observed, “Tom looks a little beat up.” Someone else added, “He’s almost unrecognizable…she must be concerned!”
Another Hollywood icon generating buzz with his new appearance is Tom Cruise. Earlier this year, the star attended a gala event in London, where his look caused quite a stir.



Leave a Reply