
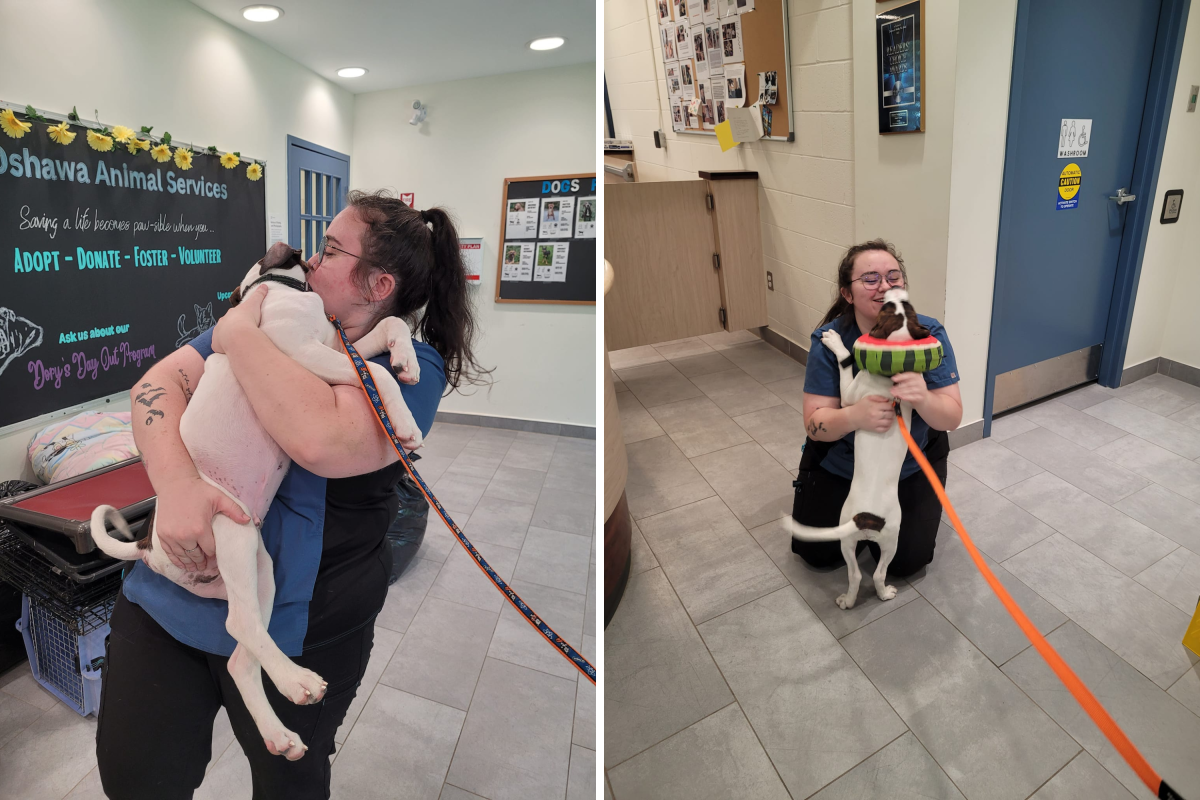
It may be hard to watch this viral video that shows the harsh reality of animal neglect. Harold was skin and bone when he was found wandering the streets in North Oshawa in Ontario, Canada. But now is thriving and just like any other puppy—thanks to his foster carer.
Kayleigh McGovern, a volunteer and team member at Oshawa Animal Services, decided to look after the emaciated dog who was too weak to even walk back in July. She documented his progress and shared a slideshow of images on her TikTok page.
Kathy Pittman-Feltham, the shelter manager told Newsweek: “Harold quickly captured all of our hearts and we were rooting for him to get healthy and find his forever home.”

In the viral video that has 791,800 views, @kayleigh_mcgovern added on-screen text to explain each image. She stated he spent the first three days in bed and he didn’t have the strength to empty his bladder.
She wrote: “We shared many cuddles, watched lots of shows, and most importantly he got lots of rest.”
One image shows Harold’s skeletal body as the on-screen text explains: “This picture is still so jarring to look at. He was examined at the vet for possible causes of his emaciation. The vets concluded the only thing wrong with him was that he was essentially starving to death.”
After a few days of tender love and care, Harold started to feel stronger and became playful. Now four months on, he is just like any other puppy.
Pittman-Feltham told Newsweek: “Kayleigh helped nurse him back to health and he was then adopted by a member of the community who is a second-time adopter from us.
“He is doing phenomenal and is the perfect picture of health.”
Harold’s remarkable transformation has touched the hearts of thousands of TikTok users. But sadly, his situation wasn’t a rare case.

Each year 6.3 million pets are surrendered to U.S. shelters, which is an average of 17,260 a day, according to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals.
Around 920,000 surrendered animals are euthanized every year. Shelters are striving to minimize euthanasia rates by promoting adoption campaigns, spaying and neutering programs, and behavior rehabilitation.
Pittman-Feltham told Newsweek: “We see many sad cases come through our doors and the team is always excited to be a part of the next chapter in their story as most times we don’t have any information on their past.
“We are hoping Harold’s story shines a light on the many cases across the rescue world that need our help.

“Fostering saves lives and Harold is a perfect example of that!“
My Husband Canceled My Birthday Dinner So His Friends Could Watch the Game at Our House — He Regretted It

On her birthday, Janine plans the perfect evening. Homemade dinner, candlelight and the quiet hope of being seen. But when her husband arrives with his friends and forgets everything, she makes a decision he never saw coming. This isn’t just a story about a ruined dinner. It’s about the night a woman finally chose herself.
I’m not dramatic.
I don’t need grand gestures or rose petals on the floor. I’ve never dreamed of surprise parties or social media tributes with sparkly filters and “I’m so lucky” captions. I don’t want to be the center of attention, twirling in a spotlight.

A pensive woman | Source: Midjourney
I never have.
But once a year, on my birthday, I believe that it’s fair to ask for a little effort. A little pause. A little something that says, Hey, I know you exist. I’m glad you’re here.
Just one evening. To feel seen.
Apparently, even that is too much.

A woman sitting at a table and holding her head | Source: Midjourney
I’m Janine. I’m the wife who remembers your coffee order, who packs snacks for your long drives, who listens, really listens, even when I’m exhausted. I’m the one who irons your shirts before your big meeting and makes sure that there’s a fresh towel when you step out of the shower.
I know the exact way you like your pie crust. Flaky, never soggy. I restock your cold meds before you even realize you’re sick. And when you’re down, I hover like you’re the last man on Earth, delivering soup like it’s sacred.
I don’t make things about me. I never have. I’ve always found comfort in the background, in the quiet flow of taking care of everyone else.

A freshly baked pie on a kitchen counter | Source: Midjourney
But this year?
I just wanted one day. One moment. One simple celebration that wasn’t something I had to build with my own two hands.
And I thought, I really thought, that he’d notice.
I sat on the porch step with a mug of matcha warming my hands, watching the last of the evening light spill over the driveway. The scent of jasmine drifted from the garden I kept alive alone, season after season.

A woman sitting on a porch step | Source: Midjourney
And I remembered another birthday.
Two years ago. A Wednesday. I came home from work to find the house quiet. No card. No cake. Just a sink full of dishes and Kyle in the den, cursing at his fantasy football stats.
“I’ll make it up to you this weekend,” he’d said, not looking up from his laptop. But he never did. The weekend came and went with errands, Kyle nursing a hangover, and a quick dinner at a noisy bar where he checked his phone between bites of pizza.

A man sitting on a couch with his laptop | Source: Midjourney
I didn’t cry then, either, in the silence of my own company. But I realized something bitter:
He didn’t forget. My husband didn’t forget. He just didn’t think that it mattered.
And that realization landed harder than any missed dinner ever could.

A woman laying in her bed | Source: Midjourney
But this year, I decided to change everything. I wanted it to be about me. I needed it to be about me.
I planned my own birthday dinner.
Not a restaurant… I didn’t want to force Kyle into anything “extra.” No reservations, no price tags, no fuss. Just a quiet evening at home with candles flickering in little glass holders.
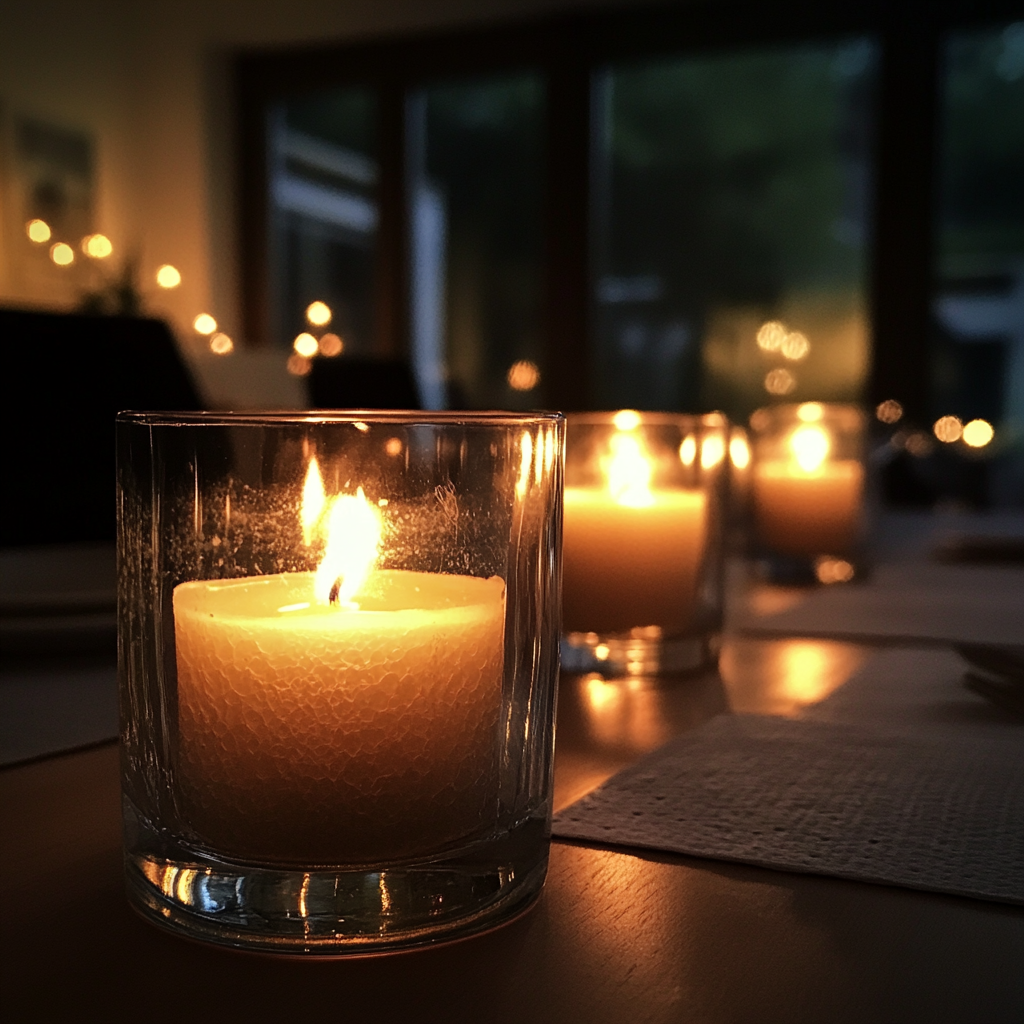

Candles on a table | Source: Midjourney
Kyle’s favorite roast lamb, slow-cooked with rosemary and garlic. A jazz playlist humming in the background. The table set with linen napkins I’d ironed that morning, polished silverware and two wine glasses we’d barely used since our anniversary three years ago.
For dessert, I made a cake from scratch. Lemon zest and almond cream because when we were still dating, my husband had mentioned that flavor reminded him of his grandmother. He’d only said it once, in passing.
But I remembered.
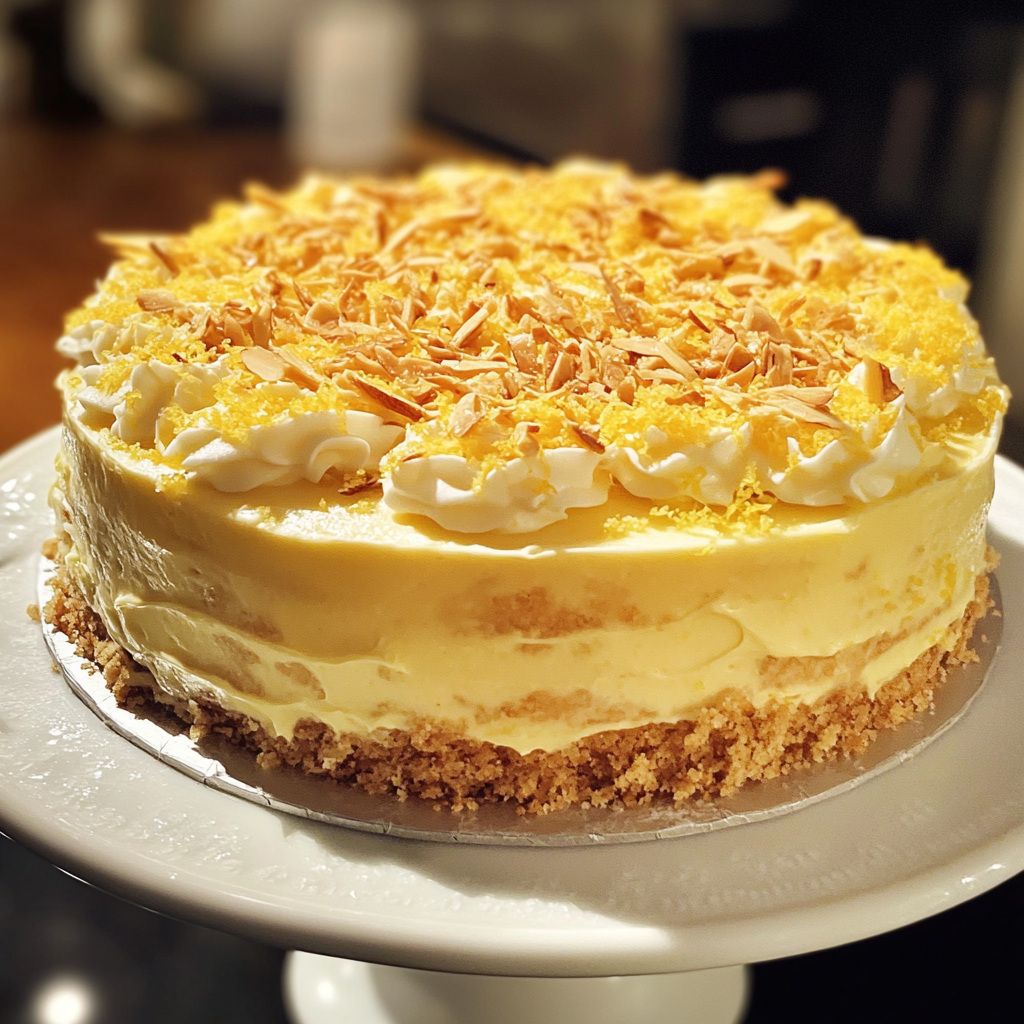

A cake on a platter | Source: Midjourney
I even bought myself a new dress. Navy blue. It was fitted at the waist, soft against the skin. I curled my hair, put on a touch of lipstick and dabbed the perfume he bought me four Christmases ago. The same perfume that I’d only worn twice.
It smelled like hope to me.
I wanted to be seen. Not in a social media post way. But in a “my husband actually notices me” way.
Which is why I planned the entire thing… for my birthday.
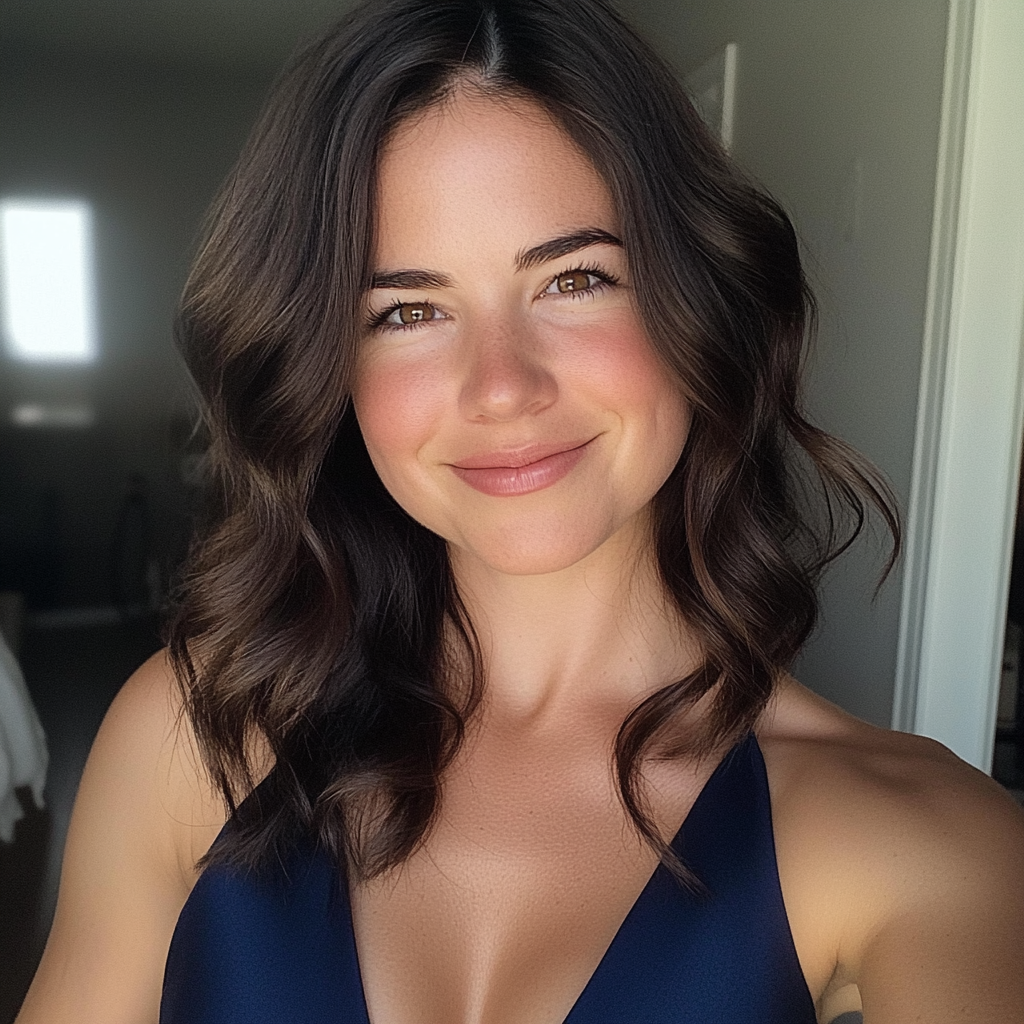

A smiling woman wearing a navy dress | Source: Midjourney
By the evening, everything was ready. The lamb rested on a serving dish. The wine was chilled. The mint sauce was in a little white bowl. The cake was cooling under a glass dome.
I checked the clock. Rechecked the table. Adjusted the vase of tulips. Smoothed the front of my dress with slightly shaking hands.
And then, the front door opened. Laughter, loud and thoughtless, spilled down the hall.
A vase of tulips on a dining table | Source: Midjourney
The smell of greasy pizza took over the house. The thud of boots not wiped at the door. The air had shifted immediately.
Kyle walked in, laughing with his friends. He was balancing two twelve-packs and three pizza boxes. Behind him were Chris, Josh and Dev. Kyle’s game-night crew. They called out greetings, already halfway to the couch.
No “happy birthday.” No flowers. Not even a glance at the candles I’d lit or the silverware I’d polished. Just noise, beer and the sound of something inside me quietly folding in on itself.
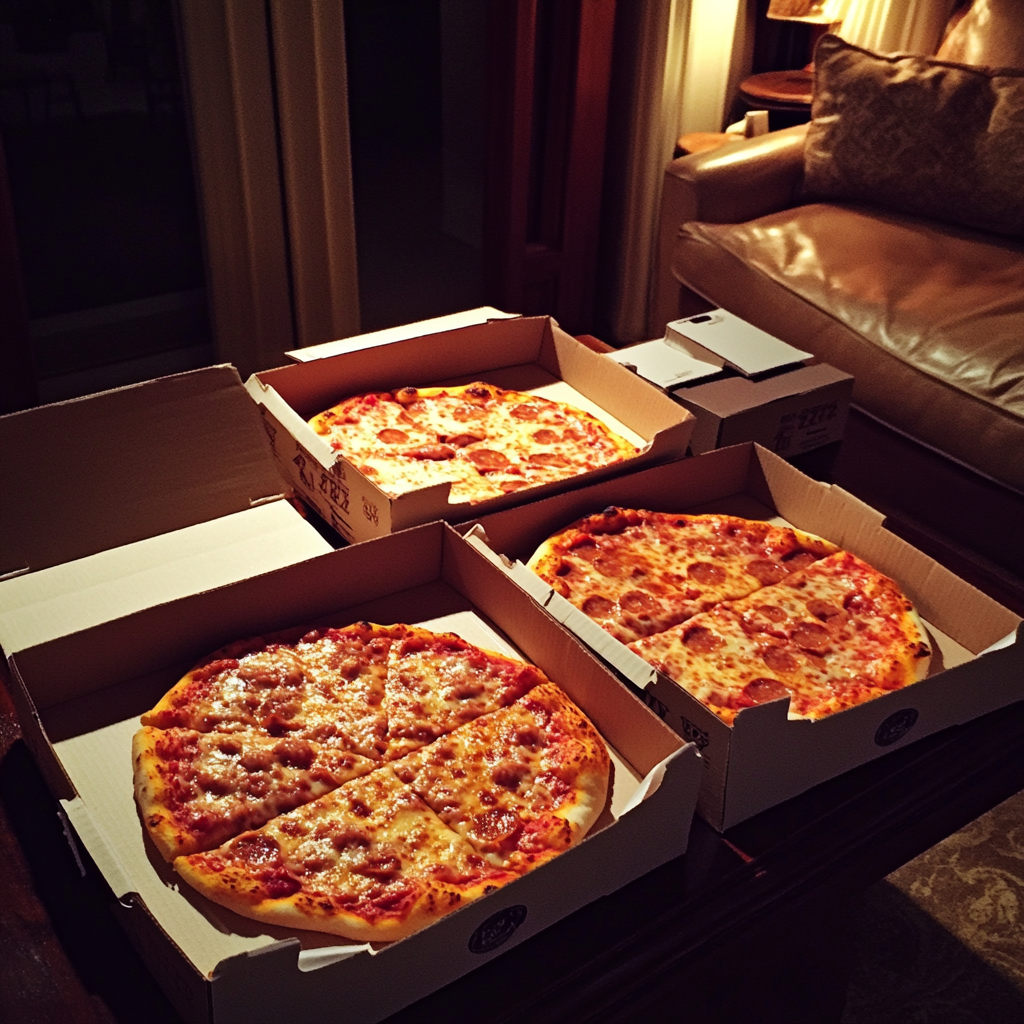

Boxes of pizza on a coffee table | Source: Midjourney
“Kyle?” I called. “Come here a sec?”
He sighed and walked toward me.
Kyle looked at the table and paused.
“Oh, right…” he said slowly. “This was tonight, huh? Yeah, we’re going to have to reschedule, Janine. The guys are here to watch the game.”
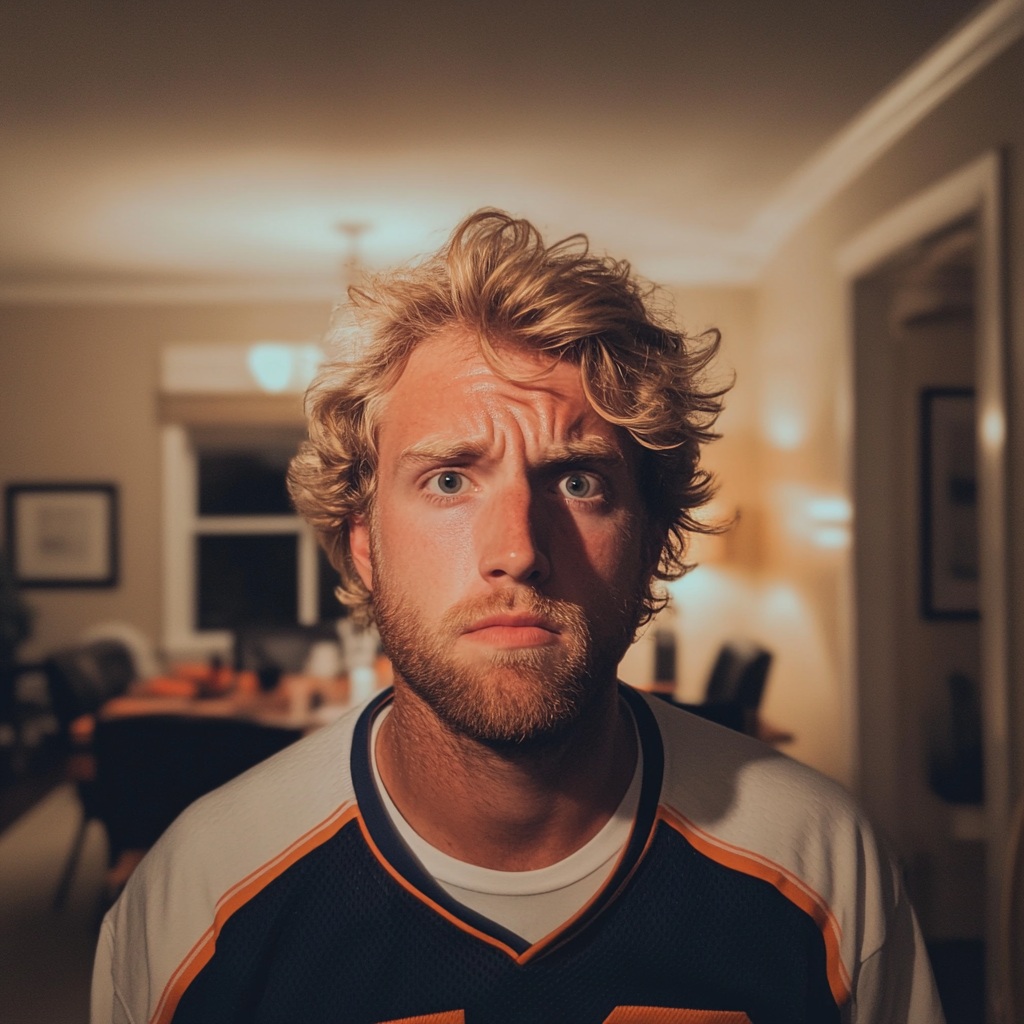

A frowning man wearing a sports jersey | Source: Midjourney
There was no apology. No hesitation. Just a lazy shrug and a look toward the couch.
He plopped down like he owned the room, kicked off his shoes and reached for the remote. The TV lit up in a flash. His voice rose over the music I had carefully chosen. He cracked a beer and held it up like a trophy.
I just sat there, at the dining table, trying to understand when I’d lost my husband.

A pair of boots on the floor | Source: Midjourney
“Starving, babe,” he said a few minutes later, standing right in front of me. “I’m taking the lamb. Looks delicious. There’s pizza if you want.”
He took the roast lamb and started picking at it. The one I’d basted and brushed every half hour. The one I made to feel like a hug on a plate.
Josh came to the table and grabbed the bowl of roast potatoes. Chris poured wine into a red Solo cup. Dev joked about the candlelight, calling it “romantic for a dude’s night.”
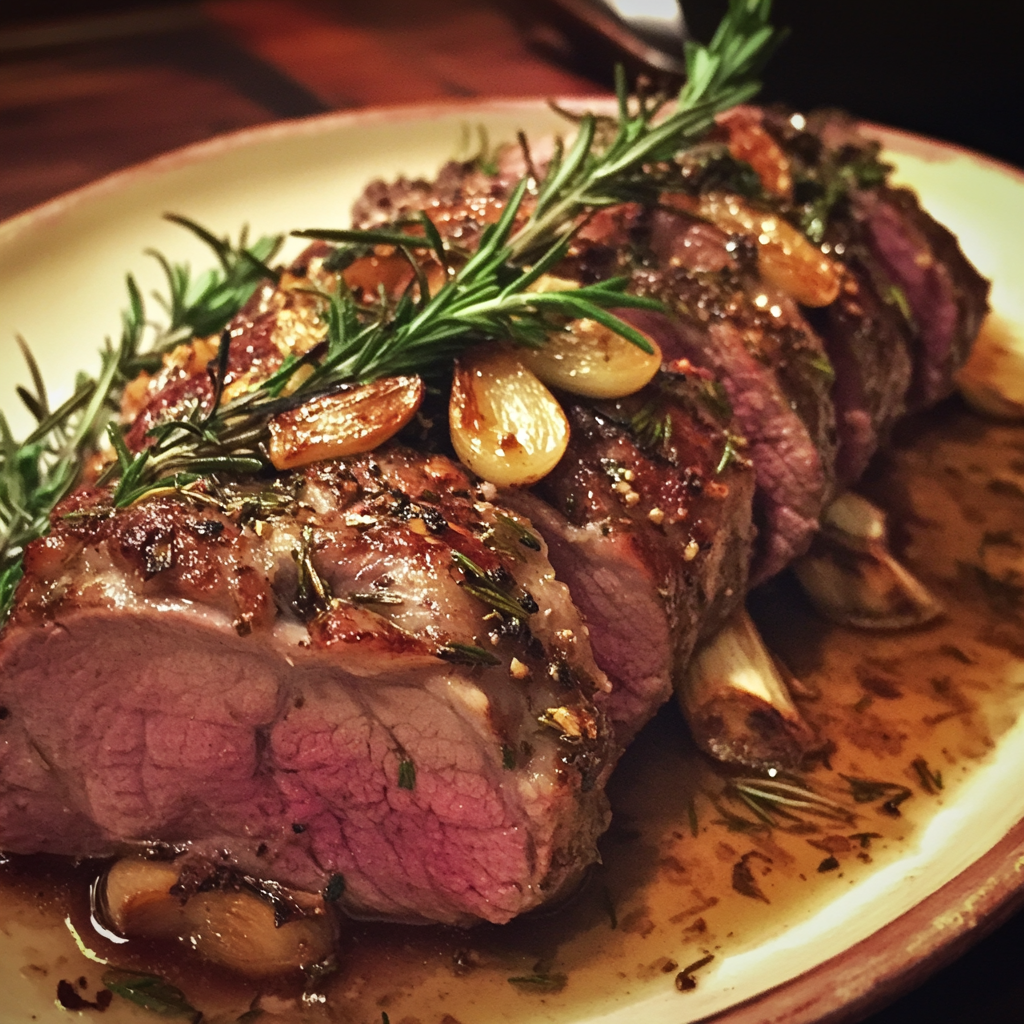

A platter of roast lamb | Source: Midjourney
I stood in the doorway, hands at my sides, watching.
Watching the napkins I’d ironed crumple beneath greasy hands. Watching the food I’d made for myself, on my own birthday, disappear into paper plates and careless mouths.
Watching my night die in real time. In front of me.
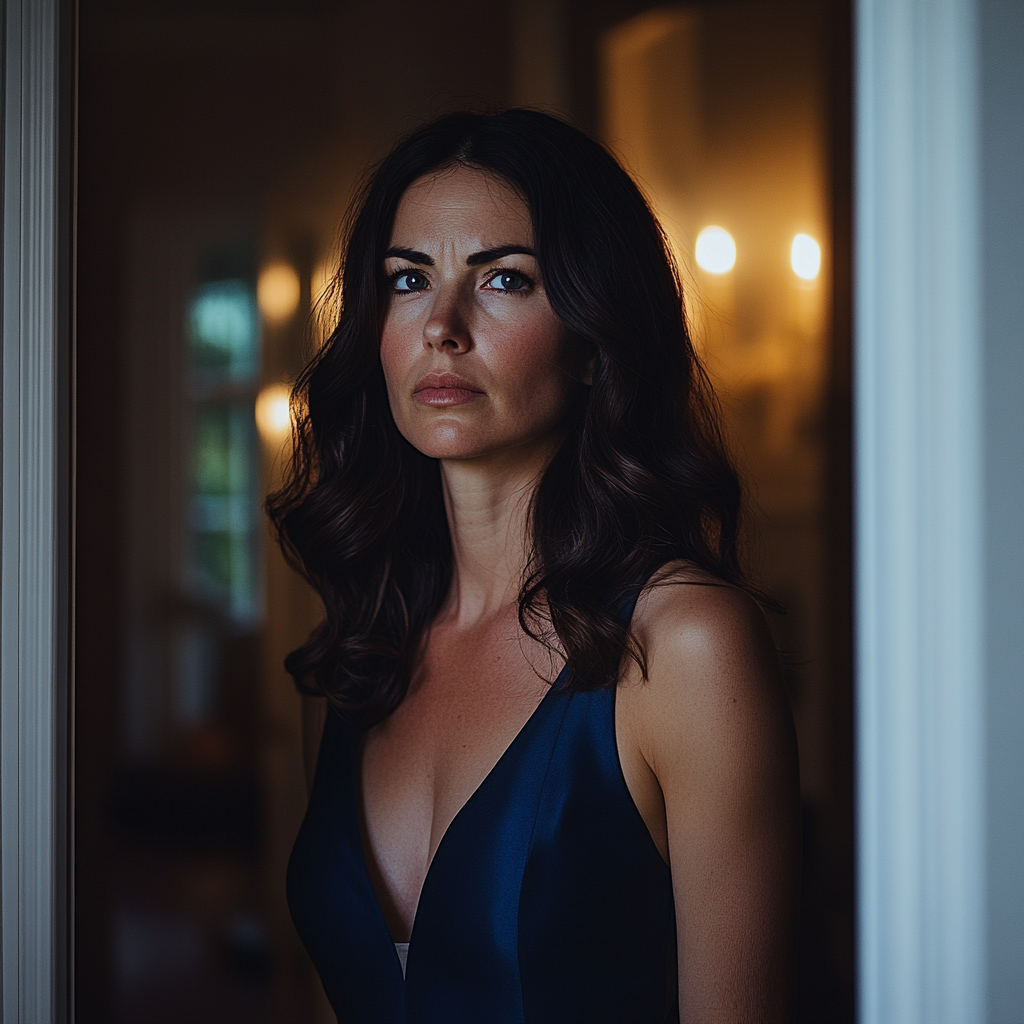

An upset woman standing in a doorway | Source: Midjourney
But I didn’t cry. I didn’t scream.
Instead, I smiled. A small, hollow thing.
“Wait,” I said calmly. “I made something really special for tonight. Just give me five minutes, okay?”
They nodded, barely looking up, thinking I probably had dessert or some party trick coming. They went back to their chatter and chewing.

A man holding a plate of pizza | Source: Midjourney
But that was it. I wasn’t having it anymore. Enough was enough.
I walked to the laundry room. I opened the fuse box. Took one last deep breath and shut everything down. The power, the Wi-Fi, the backup router.
All of it.
The house dropped into sudden darkness. The TV cut off mid-commentary. The fridge stopped humming. The only sound was the dull confusion rising in the dark.
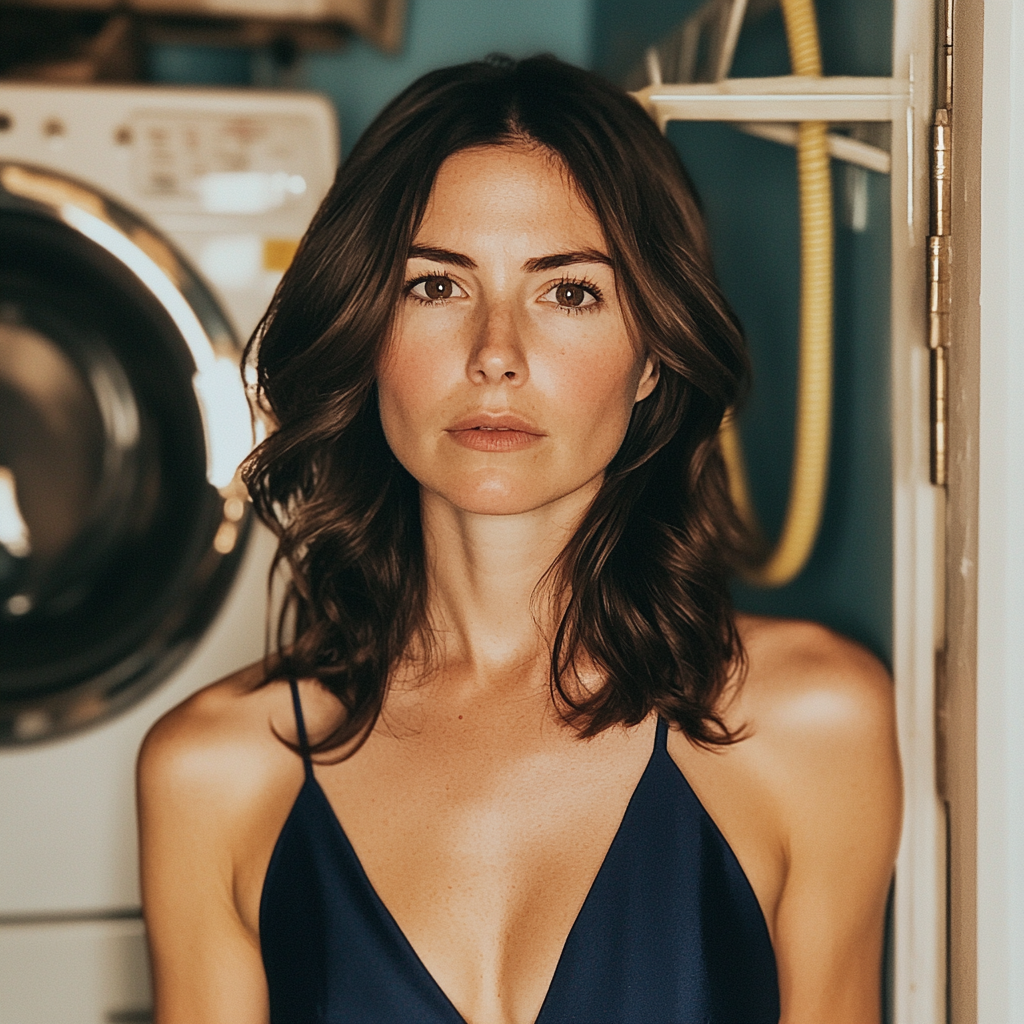

A woman standing in a laundry room | Source: Midjourney
“Babe?!” Kyle’s voice echoed down the hall.
“What happened?” I asked.
I returned to the kitchen with a candle in hand, illuminating the untouched birthday cake still glowing on the counter like a soft little rebellion. I picked up my phone and texted my parents.
“What’s going on?” Josh mumbled.

Candles on a dining table | Source: Midjourney
“Power outage,” I said simply. “You’ll probably have to call someone. Might take a few hours.”
Then I packed the rest of the food, well, what hadn’t been mauled, into containers. I slid them into a tote bag, grabbed my coat and keys and walked right out of the door.
No one stopped me.

Leftovers in a container | Source: Midjourney
I drove to my parents’ house. My sister was there. So were a few old friends from the neighborhood. There were balloons. Gifts. A hand-drawn banner. A cake from the 24-hour bakery. How they managed to do all of that in the 30 minutes it took to get there, I’ll never know.
There was music that didn’t make my ears ring. There was no loud sport commentary. There was laughter that didn’t feel forced.
There was a seat, just for me.

A birthday cake on a table | Source: Midjourney
And for the first time in years, I felt celebrated.
I laughed. I danced. I ate a slice of cake that didn’t taste like obligation. There were candles, hugs, stories from old friends who still remembered the girl I used to be. For once, I didn’t feel like an afterthought. I felt like Janine, not someone’s wife, or someone’s “MVP.”
I was just… me.

A smiling woman sitting at a table | Source: Midjourney
I got texts, of course. Missed calls. Kyle even left a voicemail. His voice was laced with confusion more than concern.
“You’re seriously mad, Janine? Over dinner? Call me back.”
I didn’t.
But I returned home the next morning.

A cellphone on a table | Source: Midjourney
Kyle was in the kitchen, arms crossed, his foot tapping against the tile like he’d been practicing his speech.
“Seriously?” he snapped the moment I walked in. “Cutting the power? Over a missed dinner? I was still in the house! We were sharing the dinner with my boys! That was just so dramatic, Janine.”
His tone was all accusation and zero apology. Like I was a child who’d flipped a Monopoly board instead of a woman who’d finally run out of patience.

An annoyed man | Source: Midjourney
I didn’t answer. Just slipped off my coat, set down my bag and pulled out a neatly wrapped box from the tote.
“What’s that?” he blinked.
I handed it to him without a word. He tore at the wrapping, the irritation still clinging to him.
Then he saw what was inside.

A box on a table | Source: Midjourney
Divorce papers. They weren’t real, yet. I hadn’t had the time to get real papers drawn up. This was something I’d downloaded off the internet at my parents’ house. There were no names on it but I figured that it would get the message across.
Kyle’s hands froze mid-flip. His brow furrowed as he scanned the top page, as if some fine print might reveal it was a joke.
“You can’t be serious,” he said finally, his voice quieter now. Less sure.
I looked at him, really looked, and saw a man so used to being prioritized that it never crossed his mind that I might choose myself.

Divorce documents on a table | Source: Midjourney
“You’re right,” I said, my voice soft. “I wasn’t serious. Not about dinner. Not about birthdays. Not about me. I stopped being serious about what I needed a long time ago, Kyle.”
I paused, taking a deep breath.
“But I’m done being the only one who cares.”
I walked past him, the click of my heels the only punctuation I needed. I didn’t look back. But as I reached the doorway, I stopped.

A frowning woman wearing a sweater | Source: Midjourney
I pulled the candle from my bag, the one that had stayed lit through dinner, through the drive, through the quiet.
I walked back into the living room, set it gently on the windowsill and lit it. Its glow was steady. Small. Defiant.
Kyle stood behind me, confused.
“The power’s back,” he said stupidly.
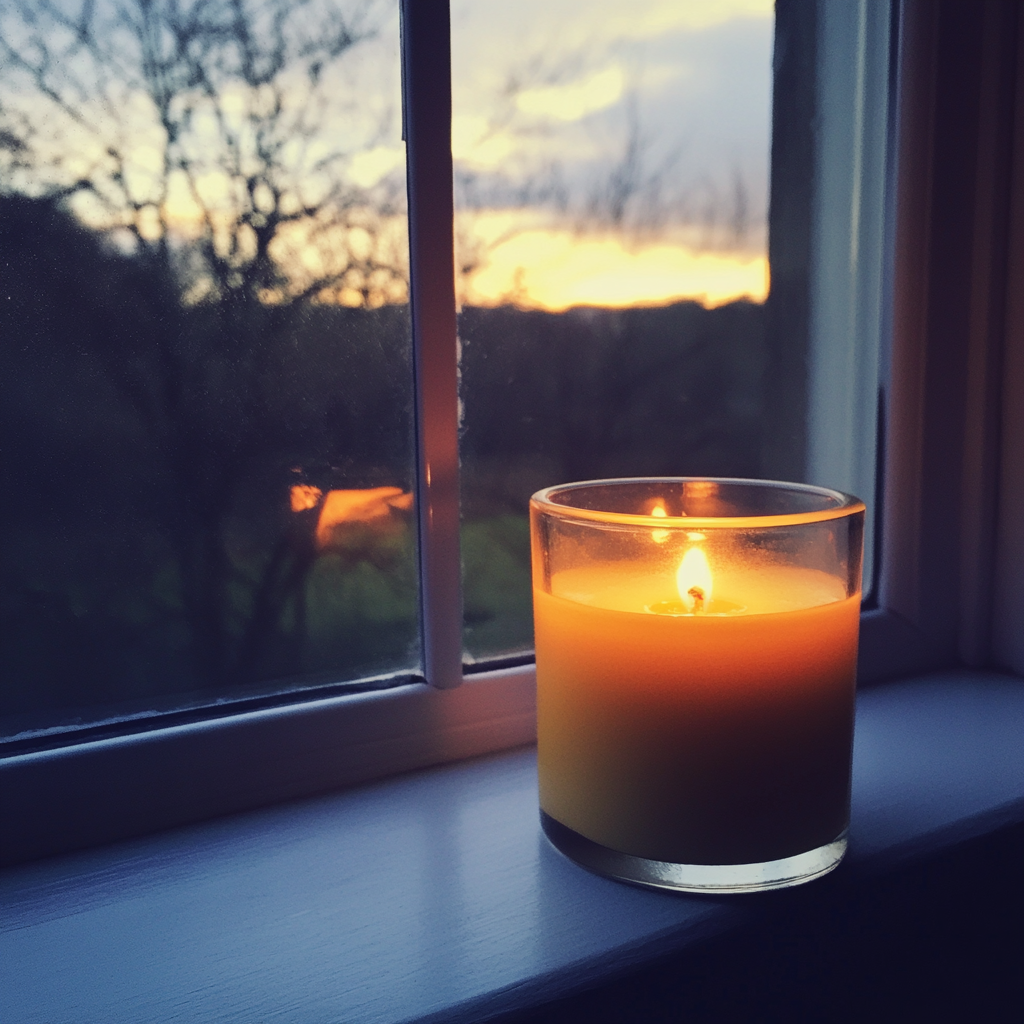

A candle lit in a windowsill | Source: Midjourney
“It’s not about that. It’s not for that. I don’t need the power back on,” I said. “I found everything I needed in the dark, Kyle.”
And then I left. No speech. No slam of the door.
Just the quiet sound of a woman choosing herself for the first time in far too long. I’m not sure what game they were watching that night… but I know who really won. Because I may have walked out with cold leftovers and one flickering flame. But I also walked out with my dignity.
And I never looked back.
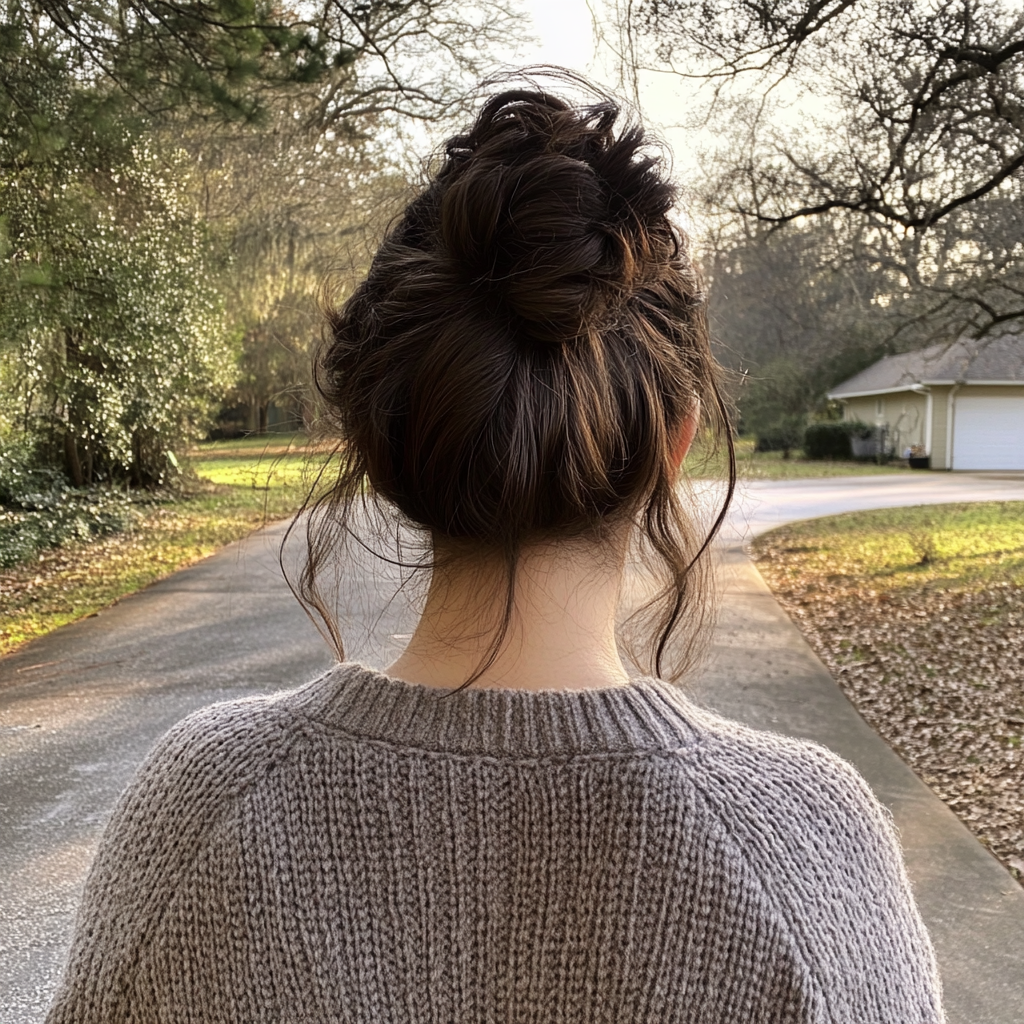

A woman walking down a driveway | Source: Midjourney
What would you have done?
If you’ve enjoyed this story, here’s another one for you |
When Liv’s husband ambushes her with a surprise dinner for his boss, she’s expected to perform domestic magic on command. But Liv is done being invisible. With one petty-perfect plate, she flips the power and makes him see the fire behind her smile. Sometimes, revenge is best served on toast.



Leave a Reply